Defining Agentic AI
The way we work is rapidly evolving, and AI is no longer just a tool for data analysis or customer support. It is now capable of executing entire workflows autonomously. AI agents capable of navigating applications, typing, clicking, and problem-solving autonomously. This is the promise of Agentic AI, and it’s redefining the boundaries of automation.
Agentic AI refers to a class of AI systems known as intelligent agents. Unlike traditional software, which follows a fixed set of instructions, an intelligent agent can perceive its environment, reason about what it perceives, and take actions to achieve specific goals.
An intelligent agent works in a loop:
- Perceive: It gathers data from its environment (e.g., observing a user interface or receiving a command).
- Reason: It processes this data, considers the goals, and decides on an action.
- Act: It takes the chosen action, such as clicking a button, generating a report, or sending an email.
- Learn: Advanced agents improve over time by learning from outcomes and feedback.

For example, think of an automated customer support system. It monitors incoming support tickets (perception), categorizes them based on urgency and topic (reasoning), and routes them to the appropriate team or generates an initial response (action) to resolve the issue (goal). While simple, this is a basic intelligent agent that demonstrates how perception, reasoning, and action align in an enterprise workflow.
The concept of intelligent agents isn't new. Agents were quite a popular research topic in AI in the ‘90s and early 2000s.
Back then, agents were often simple systems that used predefined rules to automate tasks. These traditional agents could perform actions, but their capabilities were limited to what was explicitly programmed. They followed a rigid decision tree: if X happens, do Y.
These systems were prone to breaking under the slightest changes, requiring constant maintenance and reprogramming.
LLMs as the Agent Brain
The recent advances in generative AI and large language models (LLMs), enabled modern Agentic AI and represents a significant leap forward.
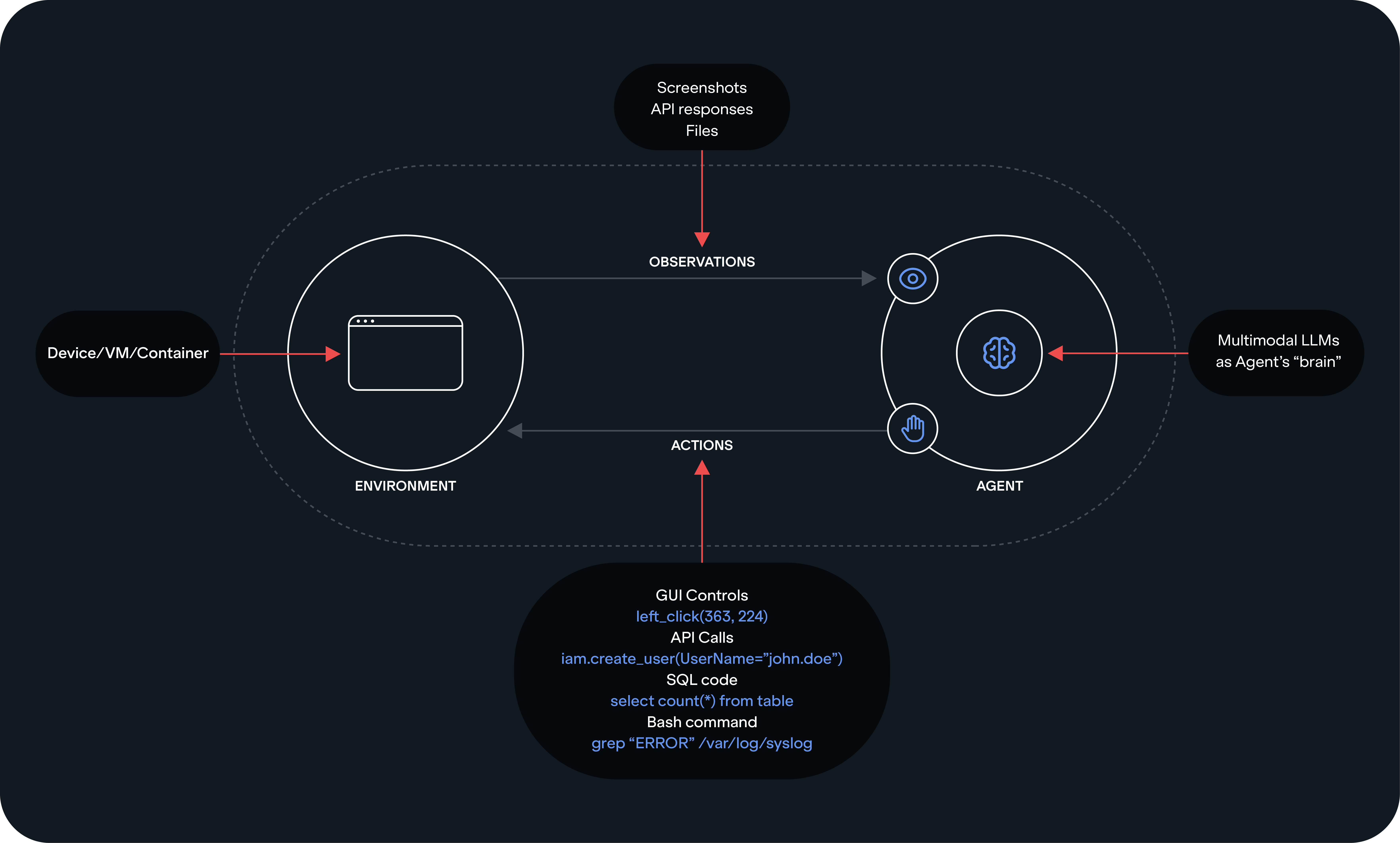
LLMs serve as the “brain” of the agents:
-
Perception: Agentic AI perceives its environment through sensors such as text inputs, screenshots, or even real-time data from applications. For example, it might "see" the layout of a webpage or interpret a user's command.
-
Reasoning: This is where the magic of LLMs comes in. These models process the information they receive, and while generating text tokens, reason about it, and make decisions. For example, an LLM might determine that an error message on a screen means it should retry an action or alert the user.
-
Action: The agent executes actions coming from the “brain” like interacting with APIs, clicking buttons, moving a mouse, entering text, or operating a robotic arm. It can complete complex workflows such as automating security checks, invoice processing or generating compliance reports.
-
Learning: Advanced Agentic AI systems incorporate feedback loops. It can learn new skills or operate new tools as they become available. If an action fails or produces incorrect results, the agent can learn from user input and adjust its behavior over time.
![]()
Agentic AI builds on the foundation of intelligent agents but integrates the capabilities of LLMs to unlock entirely new possibilities. Instead of just following predefined rules, these agents can understand natural language, learn from examples, and operate autonomously in dynamic environments, much like a team member who progressively learns on the job.
Agentic AI vs. Conventional Automation
Modern work has become digital-first, yet many of us spend hours every day sunk in repetitive tasks like data collection, searching and entry, report generation, and form submissions. This phenomenon, commonly referred to as "death by 1,000 clicks," has led to widespread inefficiencies.
For example, in large enterprises, workflows like employee onboarding or ingesting customer contracts into an ERP demand significant human resources. At scale, this results in wasted hours, bottlenecks, and burdensome operational costs.
Traditional solutions like Robotic Process Automation (RPA) emerged to address this challenge. While RPA provides some relief, it has its limitations:
-
High setup costs: Encoding workflows into RPA bots requires specialized expertise and months of setup time.
-
Brittle execution: RPA bots rely on hard-coded rules, making them prone to failure when workflows change.
-
Burdensome maintenance: Bots require continuous monitoring and frequent updates, defeating the purpose of automation.
Agentic AI, by contrast, is designed to learn by example and adapt dynamically, allowing it to flexibly manage tasks even in a fast-changing environment.
This is what makes Agentic AI the ideal solution for today’s dynamic enterprise environments, where adaptability and scalability are crucial.
Key Advantages of Agentic AI
-
Adaptability: Unlike traditional systems, Agentic AI doesn’t need rigid programming. It can handle variations and uncertainties, such as when a button moves on a screen or a process requires an unexpected step.
-
Multi-step Reasoning: It can break down complex workflows into manageable steps, execute them sequentially, and adapt if something goes wrong.
-
Generalization: LLMs can learn tasks "on the fly" without requiring extensive retraining. This is known as in-context learning. When provided with a few examples or instructions in natural language or images, the model generalizes from them to complete new tasks.
-
Proactivity: It doesn’t just react to use commands like a copilot. It proactively anticipates what’s needed and takes initiative, whether that’s an under specified prompt, error correction or learning from user input.
For CIOs and business leaders, Agentic AI represents an opportunity to future-proof operations, improve productivity, and gain a competitive edge.
What's Next in the Series?
This post introduced the concept of Agentic AI and its foundational building blocks.
In our next post, we'll dive deeper into the technology powering these systems - Large Language Models (LLMs). We'll demystify terms like “RAG”, "in-context learning" and "chain-of-thought reasoning" to help you understand why LLMs are the brains behind Agentic AI.
Stay tuned as we explore how Agentic AI is revolutionizing industries and how your organization can harness its power.
Agentic AI isn't just the future of automation - it's the future of work.
Are you ready to embrace it?
Cheers,
Pedro Saleiro,
Co-Founder/Chief AI Officer


